
Photo by Teleyinex
Web Literacy in Adults
An Educational Approach Using Game Mechanics in Curriculum to Teach Web Literacy in Adults
by Laura Hilliger
A Master Thesis Presented to the Zentrum für Qualitätssicherung in Studium und Weiterbildung of the University of Rostock. In partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Arts in Media and Education
Photo by Cisco
We live in a digital world.
- Our global knowledge ecosystem is the World Wide Web
- The Internet has become an important piece of our infrastructure
- We use the Internet to communicate, to work, to make decisions
- We need it to fully participate

Understanding the Web is a part of being educated.
- You are educated when you can think critically about key problems (Klafki)
- The Web holds the world's information and humanity's knowledge
- It gives us an infrastructure to consider those problems and to help solve them

Technology keeps changing on us
Many people are not participating in the global exchange of knowledge, which supports us in thinking critically about key problems because they lack the skills to do so

We're working on it
- Education systems have begun using various technologies in the classroom, but educators are not necessarily competent in this area.
- Adults are responsible for the education of the next generation
- It isn't just about the use of technology, but the sharing of knowledge
- Only 29% of adults between 30 and 50 have ever contributed knowledge to the global knowledge network
- Web Literacies are a vital part of our educational endeavors, so educators need to possess web literacies

Using a Pragmatic Approach
- I wanted to contribute knowledge
- I wanted to link theory and practice
- I did not want to get hung up on strict rules
- Working pragmatically allowed exploration, flexibility and discovery
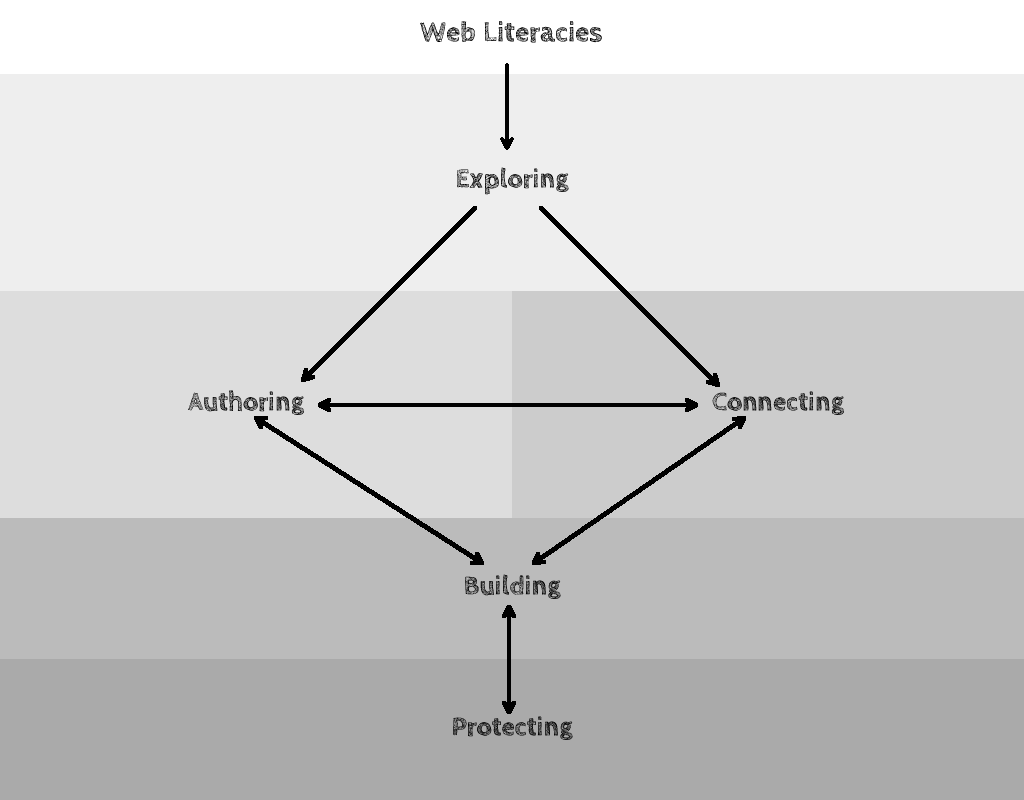
Finding a definition for "Web Literacies"
Thanks to Dr. Doug Belshaw, Common Sense Media, Scratch, Michelle Levesque, Jeanette Wing and many more

Photo by Matt Thompson
Learning through Making
- Interest driven, project based learning
- Connecting head and hand
Gamification
- Motivation
- Practice
- Intensity
- embedded assessments and other game mechanics
4 Levels at which Blended Learning can occur

Khan's Octagonal Framework for Meaningful E-Learning Experiences
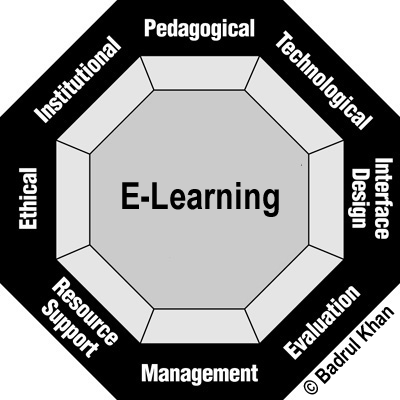
Graphic by Badrul Khan

Combining Methodologies
- Interest Driven, Project-based Learning
- where Khan's 8 Dimensions are considered
- on each Blended Learning level
- and content uses game mechanics

Training the Teacher
- focuses on educators working in Film and Media (interest driven)
- has projects to complete (project based)
- blends on each level, and in each dimension
- and content uses game mechanics
Learning Objectives
- The first three groupings of web literacies
- Web Native Filmmaking from the beginning
- Tools and Techniques
- Using the new knowledge in the classroom
OERs
- Modular Content
- Constituent Co-Designed
- Feedback Loops
- Rapid Prototyping
- Playtesting

Online Learning and Support with In-Person Workshops
- Each level blends both the production and consumption of learning materials
- various workshop formats target introductory, instructional or practical knowledge acquisition
- in-person crash courses
- online and offline materials

Six Weeks of Blended Learning
- Partner Organizationen führen Präsenzveranstaltungen
- Baseline Materiellen für jeder Partner Organizationen ist das gleiche, aber da ist noch flexibilität
- Wir stützen uns gegenseitig an und Lernenden können sich jeder Zeit mit alle Beteiligte austauschen
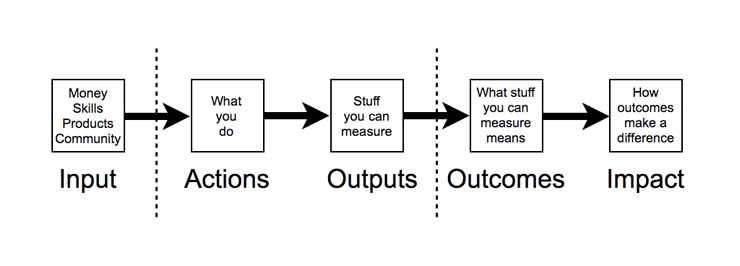
Evaluation
- Modularized and co-designed content = the need for ongoing evaluations
- Evaluations take place on all four levels
- Peer Based
- Formative
- Summative